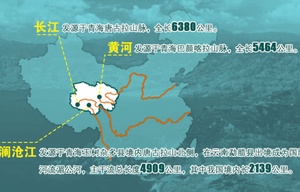
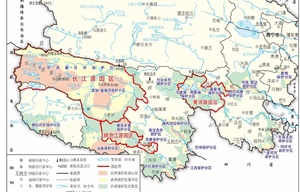
Located in the hinterland of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, with an average altitude of over 4,000 meters and a total area of 395,000 square kilometers, the Sanjiangyuan area is an important water source for China and even Asia. The Yangtze, Yellow, and Lancang Rivers all originate from here. The Yangtze and Yellow Rivers are the mother rivers of the Chinese nation and the Lancang River is an important international river that flows through six countries.
The total drainage area of these three rivers is close to one third of the total area of China. 700 million people reside within the basin, accounting for more than half of the total population of China. To a certain extent, the three rivers have laid the foundation of lives for the Chinese people. However, 25% of the total water flow of the Yangtze River, 49% of the Yellow River and 15% of the Lancang River come from the Sanjiangyuan area. The Tibetan people living here are mainly nomadic herders. This way of life, which consumes very little water, frees up the space for people from downstream areas to use water.
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, where the Sanjiangyuan area is located, is the youngest plateau on the planet. Its re-creation from flat land to plateau has profoundly influenced the geographical pattern of China, making the southeastern part of China avoid the fate of desertification and become a livable “land of fish and rice”. It also helped the formation of the Loess Plateau with loose soil in the northwest as well as large water systems such as the Yangtze River, Yellow River and Lancang River.
Therefore, the Sanjiangyuan area, located in the hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, has become an important water-conserving area for China and even Asia. It is also known as the “Water Tower of China”, occupying an irreplaceable eco-strategic position due to its unique climatic characteristics, special geographical location and rich gene diversity.


Source: Sanjiangyuan Nationa Park Website